The coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) pandemic, which was attributable to the emergence of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has adversely impacted the health of individuals throughout the world. So far, over 584 million have been infected with SARS-CoV-2, of whom over 6.4 million have died.
The clinical symptoms of COVID-19 can range from cough, fever, and sore throat to mild or severe pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Study: Rational development of a combined mRNA vaccine against COVID-19 and influenza. Image Credit: taa22 / Shutterstock.com
Background
The spread of other epidemic respiratory diseases throughout the cold season increases the chance of co-infections with two or more respiratory pathogens.
One of the vital common respiratory pathogens is the influenza virus, which has previously been reported to co-infect with SARS-CoV-2. Each these viruses have similar transmission routes and cause comparable clinical symptoms after infection.
Several recent studies have suggested that influenza infection can facilitate the entry of SARS-CoV-2 inside host cells, subsequently resulting in severe pneumonia and lung lesions. Co-infection with influenza and SARS-CoV-2 has also been reported to cause severe weight reduction and a better variety of deaths in mammals. Due to this fact, there’s an urgent must develop a combined vaccine able to providing protection against each SARS-CoV-2 and influenza.
Recently, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA)-based vaccines with a lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery system have been used to mitigate the spread of SARS-CoV-2. Several mRNA vaccine candidates against influenza and other respiratory diseases are currently under different developmental stages.
A recent npj Vaccines study describes the efficacy of an mRNA vaccine known as ARIAV that encodes the hemagglutinin (HA) antigen of influenza A virus (IAV) H1N1. ARIAV was then incorporated right into a previous LNP-encapsulated mRNA (mRNA-LNP) vaccine (ARCoV) that encodes the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain (RBD) to design a combined vaccine formulation known as AR-CoV/IAV.
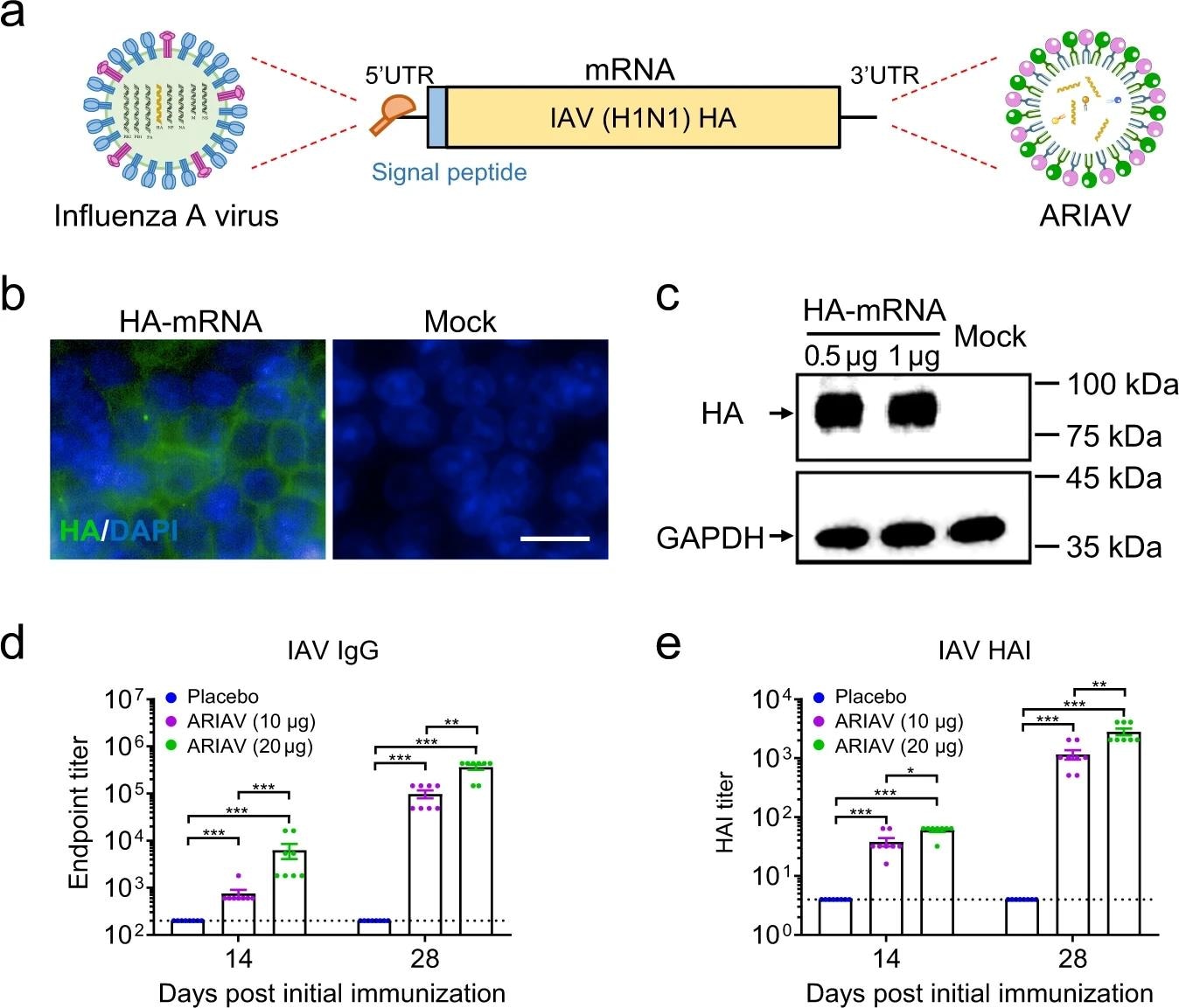 Design and characterization of ARIAV mRNA-LNP encoding HA protein of influenza A (H1N1) virus as a vaccine candidate. a Schematic diagram of ARIAV, encoding the full-length HA protein. b Indirect immunofluorescence assay of HA protein expression in HEK293T cells 48 h post-transfection. Scale bar, 20 μm. c HA expression in HEK293T cells was determined by immunoblotting. d HA-specific IgG antibody titers were determined by ELISA. e Hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) titers were determined 14 and 28 days post-initial immunization. Data are shown because the mean ± SEM (n = 8). Statistical differences were analyzed through the use of two-tailed unpaired t tests. *P < 0.05,**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Design and characterization of ARIAV mRNA-LNP encoding HA protein of influenza A (H1N1) virus as a vaccine candidate. a Schematic diagram of ARIAV, encoding the full-length HA protein. b Indirect immunofluorescence assay of HA protein expression in HEK293T cells 48 h post-transfection. Scale bar, 20 μm. c HA expression in HEK293T cells was determined by immunoblotting. d HA-specific IgG antibody titers were determined by ELISA. e Hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) titers were determined 14 and 28 days post-initial immunization. Data are shown because the mean ± SEM (n = 8). Statistical differences were analyzed through the use of two-tailed unpaired t tests. *P < 0.05,**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Concerning the study
The study involved the synthesis of mRNA that encoded the full-length HA of IAV and the SARS-CoV-2 RBD, followed by LNP formulation of the mRNA and transfection. Six- to eight-week-old female BALB/c mice were immunized with equal doses of ARIAV, AR-CoV/IAV, or placebo, which was followed by a booster dose 14 days later.
Serum samples were collected from the mice before administration of the vaccines, in addition to 14 and 28 days post-administration. Among the mice were sacrificed post-challenge with either of the viruses or co-infection with each viruses for histopathological analyses and viral detection.
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used for the detection of SARS-CoV-2- and IAV-specific IgG antibodies. Thereafter, pseudovirus-based neutralization assay, hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) assay, enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assay, and multiplex immunofluorescent assay were conducted.
Total RNA was isolated from infected mice and quantified by the quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain response (qRT-PCR) assay, followed by in situ hybridization assay. Flow cytometry was also carried out, followed by histopathological, cytokine, chemokine, and phylogenetic analyses.
Study findings
ARIAV was found to induce an HA-specific IgG antibody response, in addition to a rise HAI titers that continued to rise after booster immunization in a dose-dependent manner. Immunization with two doses of AR-CoV/IAV provided protection against IAV and SARS-CoV-2 infection.
AR-CoV/IAV was observed to activate antigen-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses, together with the secretion of several cytokines, including interleukin-2 (IL-2), tumor necrosis factor- α (TNF-α), and interferon γ (IFN-γ).
Histopathological evaluation revealed pathological changes within the lung sections following IAV and SARS-CoV-2 infections within the placebo group. Nevertheless, no pathological changes were observed in AR-CoV/IAV vaccinated mice following infection.
High levels of viral RNA were detected in each IAV- and SARS-CoV-2- infected mice receiving the placebo vaccine post-infection. AR-CoV/IAV immunization reduced the viral RNA load post-infection and conferred protection against IAV and SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Moreover, AR-CoV/IAV immunization protected infected mice from severe weight reduction. This vaccine was also found to guard against infection with the SARS-CoV-2 Alpha and Delta variants. Moreover, AR-CoV/IAV vaccination reduced the degrees of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, in addition to provided protection against IAV and SARS-CoV-2 co-infection.
Conclusions
The present study demonstrated that a combined mRNA vaccine is able to inducing broad and sturdy protection against co-infection with SARS-CoV-2 and IAV, in addition to against multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants. Further development of universal vaccines is vital to regulate the COVID-19 pandemic, in addition to the spread of other respiratory viruses.
Journal reference:
- Ye, Q., Wu, M., Zhou, C., et al. (2022). Rational development of a combined mRNA vaccine against COVID-19 and influenza. npj Vaccines 84. doi:10.1038/s41541-022-00478-w.