
In a recent study published within the BMC Medicine journal, researchers in Sweden explored the association between above-optimal maternal gestational weight gain (GWG) and the chance of neurodevelopmental disorders similar to mental disability, autism spectrum disorder (ASD), and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in offspring.
Rates of maternal weight gain over the course of pregnancy and offspring risk of neurodevelopmental disorders. Image Credit: Hazal Ak / Shutterstock
Background
Neurodevelopmental disorders are highly prevalent, and the social support requirements throughout the affected person’s life significantly burden their families. The three most prevalent neurodevelopmental disorders —ASD, ADHD, and mental disability — often present together in children.
Moreover, while de novo and inherited mutations have each been related to these neurodevelopmental disorders, other environmental, biological, and social aspects are also thought to contribute to their etiology.
Although previous studies have explored the association between maternal GWG beyond the optimal range and the elevated risk of neurodevelopmental disorders, it has been difficult to separate the consequences of above-optimal GWG and gestational duration on the adversarial outcomes related to neurodevelopmental disorders. It’s because these studies didn’t consider the length of the pregnancy as a determinant factor.
Because the growth of the functional and structural parts of the fetal brain is a sequential process and the vulnerability to external aspects similar to nutrition and environmental stressors varies across trimesters, it is important to evaluate the link between trimester-specific GWG and the chance of neurodevelopmental disorders.
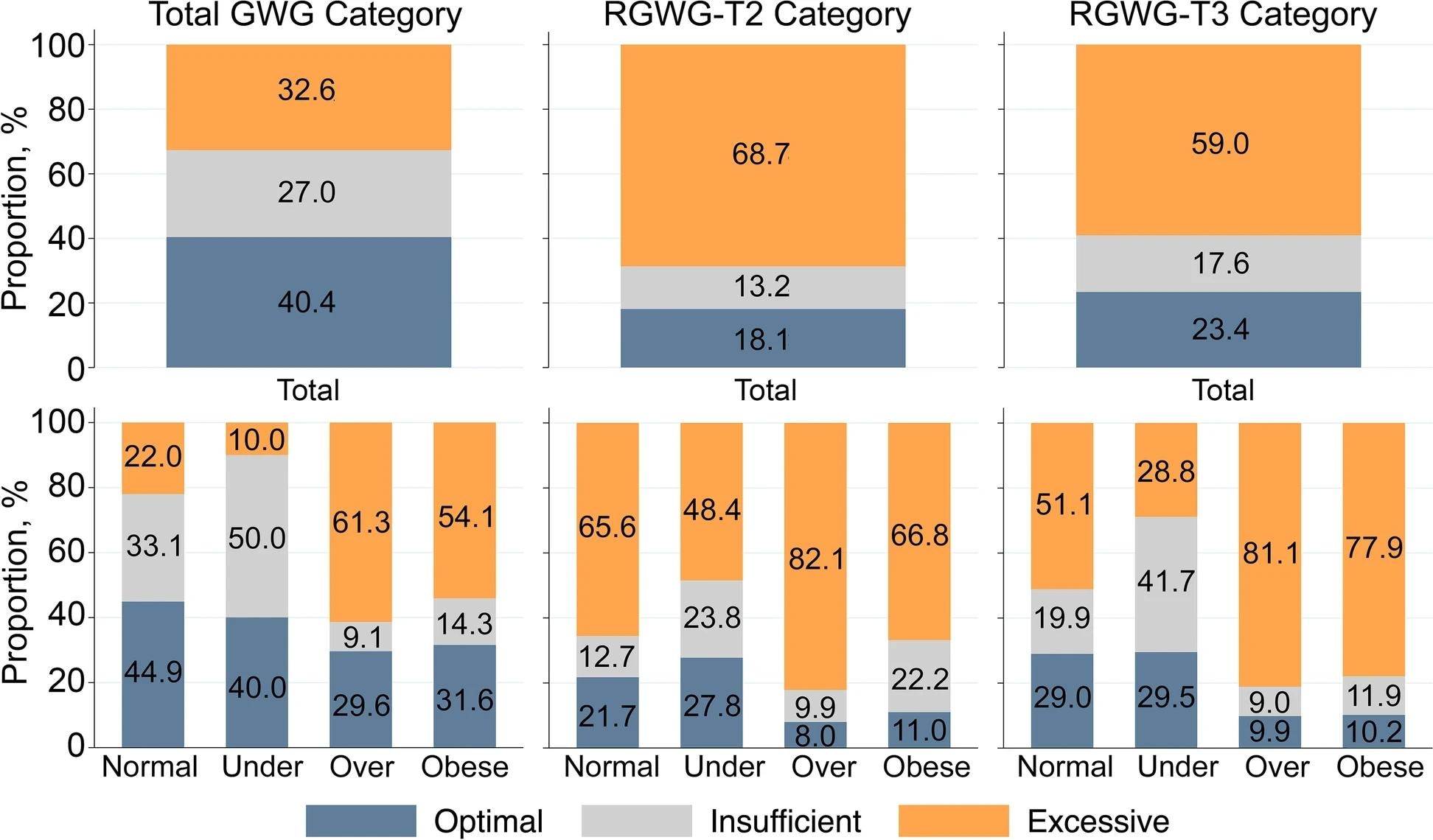 Distributions of total GWG (kg), RGWG-T2, and RGWG-T3 categories in line with the IOM guidelines
Distributions of total GWG (kg), RGWG-T2, and RGWG-T3 categories in line with the IOM guidelines
Concerning the study
In the current study, the researchers conducted a cohort study among the many Swedish population to guage the chance of neurodevelopmental disorders in line with the z-scores for GWG and the speed of weight gain through the last two trimesters of the pregnancy.
They used data from Stockholm’s record system for antenatal care and knowledge on outcomes, exposures, and covariates from regional and national health and administrative registries. Children born between January 2007 and December 2010 for whom the info on maternal GWG measurements were available were included within the study.
All neurodevelopmental disorder diagnoses were considered for the first evaluation, including one or multiple diagnoses of ADHD, mental disability, and ASD. For the secondary evaluation, the researchers only included combos of mutually exclusive outcomes similar to only ADHD or ASD, ADHD with ASD but no mental disability.
The examined exposures comprised total GWG and the speed of GWG for the second and third trimesters of the pregnancy. The evaluation was also conducted using the “insufficient,” “optimal,” and “excessive” categories for the speed of GWG for every body mass index group. Potential confounding covariates included birth 12 months, sex of the kid, household income, paternal and maternal region of birth, maternal age, mother’s education level, interpregnancy interval, psychiatric history of the mother, and smoking behavior.
Results
The outcomes indicated that higher than optimal total GWG was related to a 19% increase in the chance of any neurodevelopmental disorder, while lower than optimal GWG increased the chance of neurodevelopmental disorders by 12%.
Moreover, the speed of GWG was also related to the chance of neurodevelopmental disorders, with a slower GWG rate through the second trimester increasing the chance of neurodevelopmental disorders by 9%, but a better rate of GWG within the second trimester not being related to neurodevelopmental disorder risk.
In contrast, while a slower rate of GWG was not linked to neurodevelopmental disorder risk within the third trimester, a better rate of GWG was related to a 28% increase in the chance of neurodevelopmental disorder diagnoses.
Within the secondary evaluation using categorized rates of GWG within the last two trimesters, the outcomes reported that a low GWG rate within the second trimester combined with an excessive rate of GWG within the third trimester significantly increased the chance of mental disability and ADHD within the offspring.
The authors also discussed plausible mechanisms for linking excessive GWG and fetal neurodevelopment, similar to the downstream impact of maternal and fetal adipose tissue accumulation.
Increased adiposity within the mother and fetus is regarded as connected to dysregulations of the pro-inflammatory cytokine, insulin, leptin, and glucose signaling, increased oxidative stress, and dysregulated signaling related to dopamine and serotonin. In contrast, insufficient GWG could end in a nutrition deficit environment, which has detrimental effects on the fetus’s brain development.
Conclusions
Overall, the outcomes provided evidence that maternal GWG below and above the optimal range were related to an increased risk of neurodevelopmental disorders within the offspring. The outcomes also indicated that the speed of GWG was also a very important consider determining neurodevelopmental disorder risk.
Insufficient GWG rate through the second trimester coupled with a rapid rate of GWG within the third trimester was linked to the very best risk of neurodevelopmental disorders, especially ADHD and mental disability.
These findings suggested that the speed of maternal GWG could potentially be used as a marker to estimate the chance of neurodevelopmental disorders within the fetus.